Feel stronger , not just better
Move smarter, not harder
What we Treat
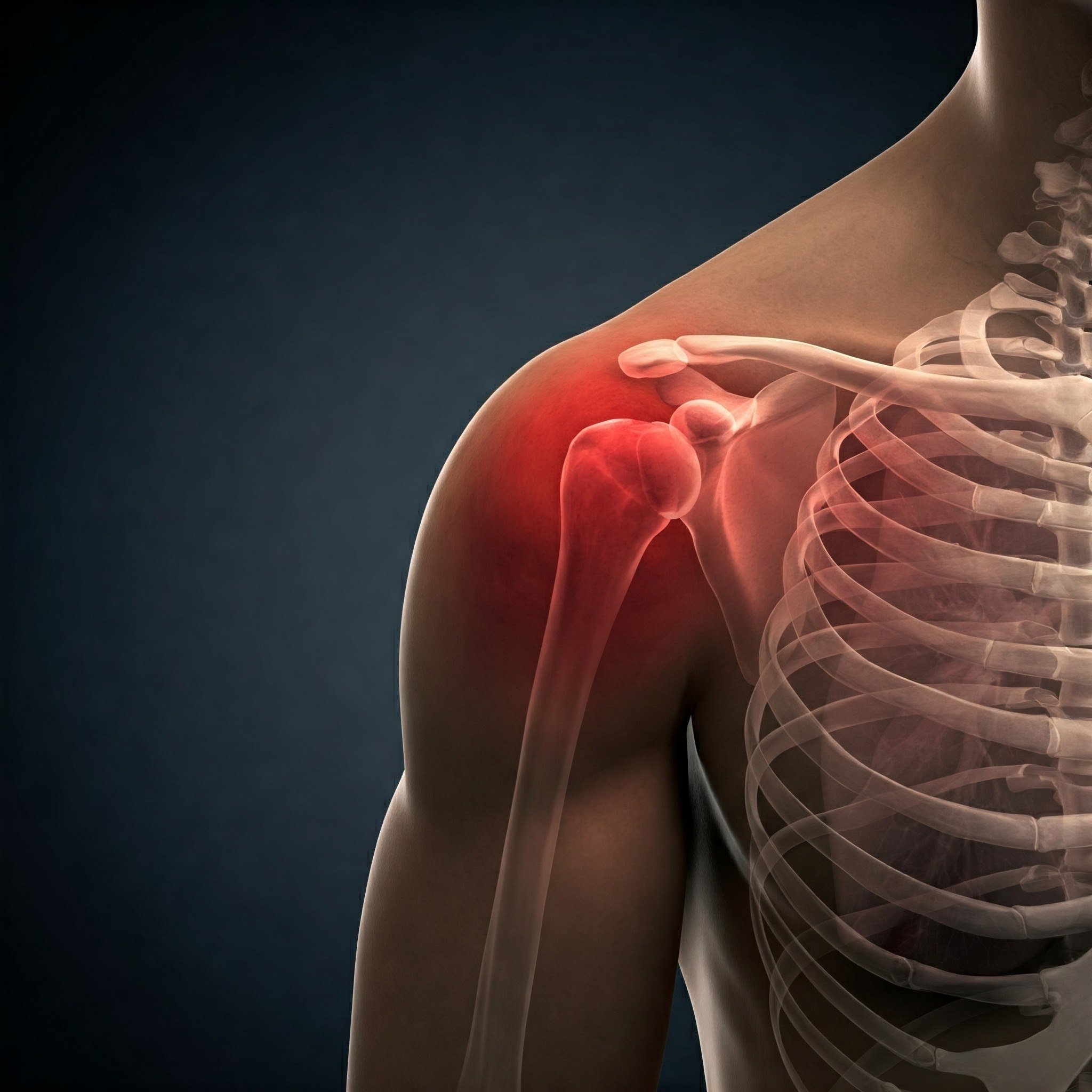
Sports Injuries
Sports injuries are a common occurrence, often resulting from overuse, direct impact, or excessive force being applied to a body part beyond its structural capacity. A variety of sports-related injuries can occur due to the strain placed on the body during physical activity. Sports injuries can be categorised into acute and chronic injuries. Acute injuries are sudden onset, typically caused by high-intensity forces and of short duration, such as sprains, strains, and contusions. Chronic injuries, on the other hand, can be divided into chronic overuse injuries and chronic recurring conditions. Chronic overuse injuries result from low-intensity forces over a prolonged period, leading to conditions like tendinitis or bursitis. Chronic recurring conditions involve repeated acute injuries, such as chronic back pain.
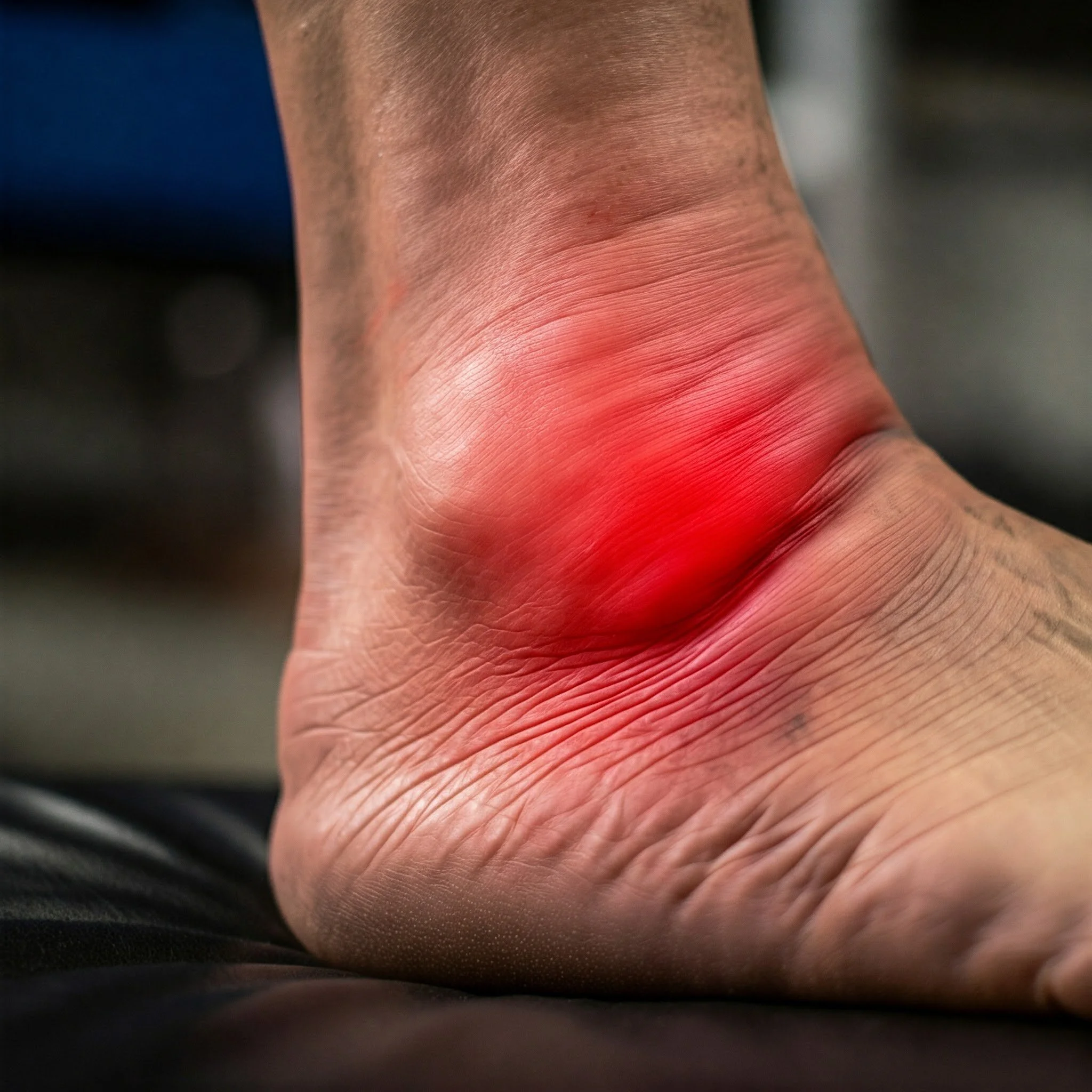
Athletes such as badminton players may experience shoulder injuries, while gym enthusiasts may suer from back pain. Soccer players are prone to acute ankle sprains, showcasing the range of potential injuries in sports. However, sports injuries are not exclusive to athletes. Individuals in various professions, such as factory workers, painters, and gardeners, may also experience similar injuries despite not participating in sports. For instance, factory workers may develop tennis elbow, painters may experience shoulder injuries, and gardeners may develop tendinitis due to the physical demands of their work.
Common Sports Injuries
Return to play / training
Return to play / return to training Recovery from sports injuries through physiotherapy involves a detailed evaluation of the injury, followed by a carefully planned rehabilitation program. This program is specially designed to facilitate a smooth return to training or play. However, one of the main obstacles to players' progress is the occurrence of recurrent injuries.
The concept of "return to play" at A PLUS PHYSIO CLINIC : Sports and Scoliosis signifies the stage in the recovery process where an individual is ready to resume sports or physical activities at a level similar to before the injury occurred, with minimal risk of further injury. Achieving this goal necessitates a holistic approach to recovery, starting from addressing symptoms through a structured rehabilitation program and honing in on essential movement fundamental skills that underpin sports performance.
These fundamental skills are refined versions of basic movement patterns, ensuring that the correct muscles are engaged and the proper movements are executed. In the realm of strength and conditioning for sports, the objective goes beyond simply gaining strength; it involves correcting any decencies in foundational movements and reducing the likelihood of injury.
Therefore, our focus lies on transitioning smoothly from healing to cultivating fundamental movement skills, which serve as the cornerstone for mastering more intricate and specialised skills needed for various sports and recreational activities. This progression is crucial for enhancing performance and preventing injuries.
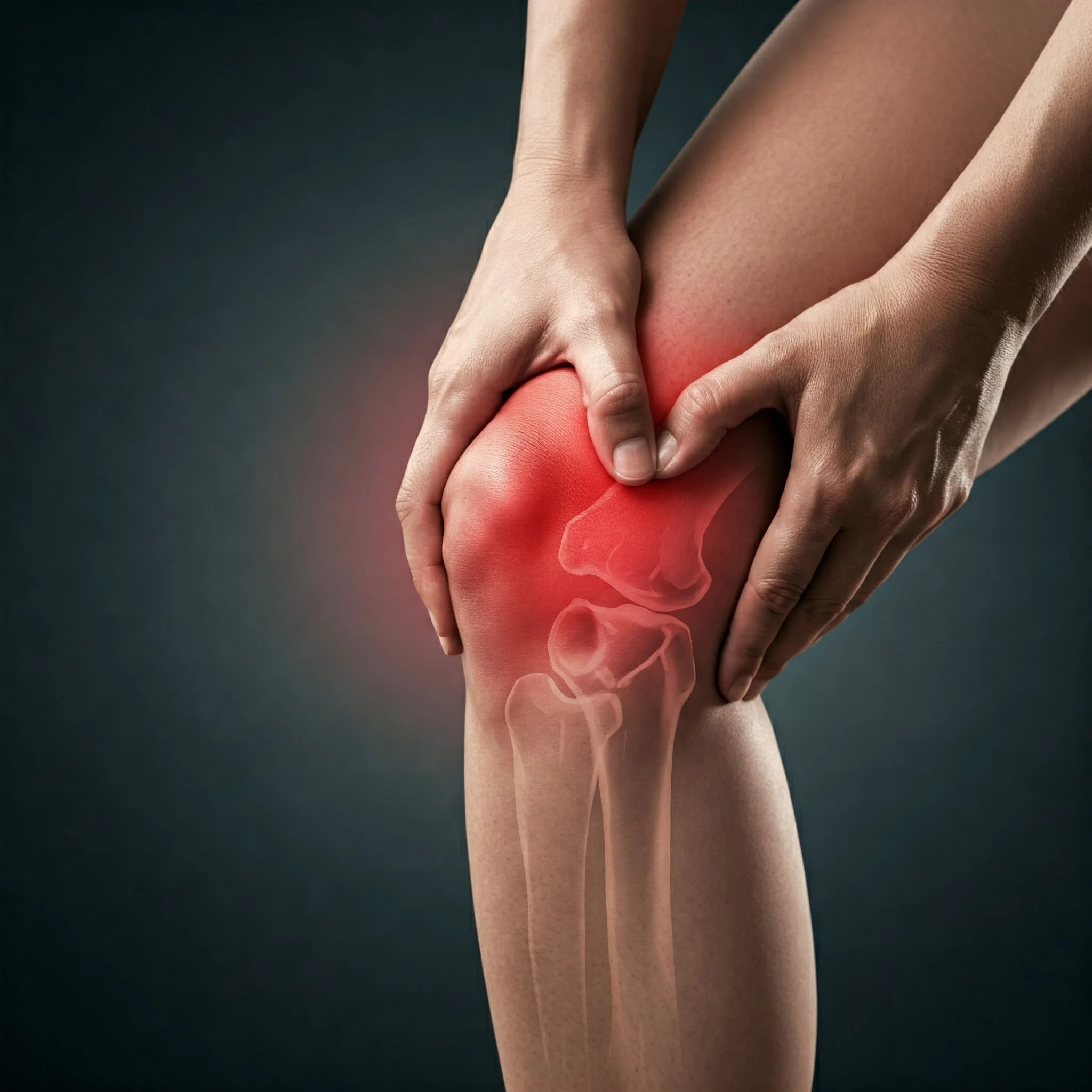
Musculoskeletal disorders
Musculoskeletal disorders are injuries or pain that impact the joints, muscles, and other structures supporting the body. These can cause mobility and dexterity issues, making it difficult to work or participate in daily activities. These disorders often result from activities like sitting for long periods, repetitive motions, lifting heavy objects, and poor posture.
Over time, these activities can lead to discomfort, pain, and potential injuries in the affected areas. As such, it is crucial to be mindful of ergonomics and proper body mechanics to prevent the onset of musculoskeletal disorders.
MSK Example
Spine Health
Scoliosis is characterised by lateral curvature and rotation of the vertebrae,
resulting in a spinal deformity. The causes of this condition are diverse and can be broadly categorised as congenital, neuromuscular, syndrome-related, idiopathic, or secondary to spinal curvature. Patients typically present with spinal asymmetry or prominence of the chest wall and back, although scoliosis may not always be immediately noticeable.
Affecting 3-5% of the population, most cases of scoliosis can be managed nonoperatively if detected early. However, approximately 60% of rapidly progressing curvatures in prepubertal children will worsen over time. Thus, screening for scoliosis is crucial to identify and treat cases before they become severe.
Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) is the most common type of paediatric scoliosis, occurring in individuals aged 10 to 18. Important indicators for identifying potential problems include young age at onset (under 10 years), rapid progression of the curvature, and neurological symptoms.
Currently, "The Schroth based method" is a popular scoliosis treatment approach, focusing on postural correction and respiratory techniques to empower patients in managing their condition.
Common Spine Problems
-
Back pain and sciatica
Back pain is a common health issue in Australia that can range from a dull ache to sharp pains. It can be caused by accidents, falls, heavy lifting, or age-related changes in the spine.
The most serious result of back pain, sciatica, causes pain that extends into the legs due to nerve irritation.
Recovery time depends on the cause, such as strain from improper lifting or structural issues like herniated disks.Seek medical advice if back pain persists or is accompanied by numbness, weakness, or other concerning symptoms.
-
SIJ dysfunction
The SIJ connects the spine and pelvis, supported by sacral ligaments and pelvic muscles, and is a common cause of low back pain when injured. This can result in significant pain in the low back and buttock area due to daily activities causing shearing, rotation, torsion, and tension forces.
Injuries to the SIJ can occur from various causes like capsular disruption, ligament tension, muscle inflammation, fractures, arthritis, and infection. Most SI joint injuries can be effectively managed with conservative treatment, with research showing over 75% of cases improving with measures like physiotherapy. -
Whiplash injury
Whiplash is a term for the forces that affect the neck when the head moves suddenly in one direction and then back again. This injury can happen in car accidents involving rear-end or side impacts, causing harm to muscles, joints, ligaments, and nerves.
Being in a car accident can result in both physical and emotional pain. Physical symptoms of whiplash may include neck pain, stiffness, headaches, dizziness, or feeling lightheaded.
Emotional reactions can include distress, anxiety, and being extra cautious while driving. In some cases, symptoms resembling PTSD may arise, leading to a consultation with a psychologist.Recovering from whiplash varies. While most people heal within a few days or weeks, others may need months to fully recover. Recovery time depends on factors like treatment methods, the cause of the injury, personal circumstances, and medical history.
A PLUS PHYSIO CLINIC can provide guidance on managing whiplash injuries and offer insight into recovery expectations.
-
Failed back surgery syndrome (FBSS)
Failed Back Syndrome, also known as Post-Laminectomy Syndrome, is characterised by persistent back pain after back surgeries. It affects about 60% of patients who have undergone these surgeries. Various factors, including preoperative conditions like anxiety, depression, obesity, and smoking, as well as psychosocial factors, contribute to the development of chronic pain in patients.
Treatment options range from conservative methods like physiotherapy to more aggressive approaches like interventional procedures or further surgeries.
At APLUS PHYSIO CLINIC, we focus on manual therapy and movement therapy improving tolerance to help alleviate back pain.
Posture correction in teenagers and children
Functional scoliosis
Functional scoliosis is when the patient appears to have a curve in their spine but it is actually caused by another condition, such as leg length discrepancy or muscle imbalance.
Functional scoliosis is often caused by leg length differences and is seen as compensatory. Contributing factors include hip dysplasia, muscle imbalances, and herniated discs. About 10-15% of teens with mild scoliosis may see their curvature worsen due to bio-mechanical changes in the trunk from factors like unevenly carrying a heavy backpack or poor posture.
Consult our scoliosis specialist before beginning any home exercises, it can help prevent the development of further symptoms.
Poor posture and spinal disorders
When we are not standing or sitting upright and engaging our muscles, when our shoulders are rounded, or our neck is moved forward, it’s showing signs of bad posture, which easily develops neck, back and shoulder pain, with increased risk of injury, stiffness and lack of concentration.
The two most common spinal disorders, Hyperkyphosis (an increase in thoracic curvature) and Hyperlordosis (an increase in lumbar curvature), are associated with significantly higher spinal loads, which may accelerate the degenerative process or lead to further dysfunction.
Physiotherapy for thoracic hyperkyphosis or lumbar hyperlordosis should be started early on and is often an effective primary treatment option, including manual therapy, taping, and movement therapy.
Prenatal and postpartum issue
Abdominal Separation
An abdominal separation refers to the widening of the normal 1-2 finger gap between the two sides of the rectus abdominis muscle located at the front of the abdomen. This condition is also known as rectus abdominis diastasis, or RAD.
During pregnancy, the body releases hormones that soften ligaments and abdominal muscles to accommodate the growing fetus. While there is typically a small gap between abdominal muscles, this gap widens during pregnancy.
Moreover, individuals may not be adequately prepared for other changes that occur during pregnancy and after giving birth, such as alterations in musculoskeletal alignment that can impact key areas of the body including spinal curvature, balance, and gait patterns.
These changes can significantly affect quality of life by causing increased back pain and an elevated risk of falls. Initiating an optimisation journey to address these changes with the assistance of our Women's Health experts is recommended, as it is never too late to start